Therapy Related Myelodysplastic Syndrome
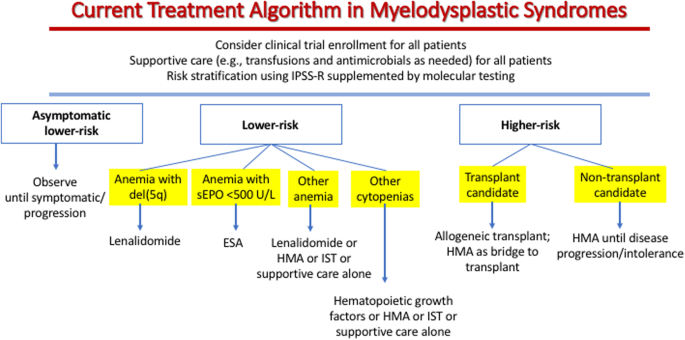
Therapy related myelodysplastic syndrome. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes or are they. A class of chemotherapy drugs may relieve the symptoms of myelodysplastic syndrome in a modest manner. Treatment for myelodysplastic syndromes includes supportive care drug therapy and stem cell transplantation.
Therapy-related myelodsyplastic syndrome NOS Effective 2001 - 2009 Reportable for cases diagnosed 2001 - 2009 Primary Sites C421 Help me code for diagnosis year. In the United States the number of new diagnoses of MDS and therapy-related MDS are both rising. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms are a consequence of conventional oncologic treatments for cancer and other conditions.
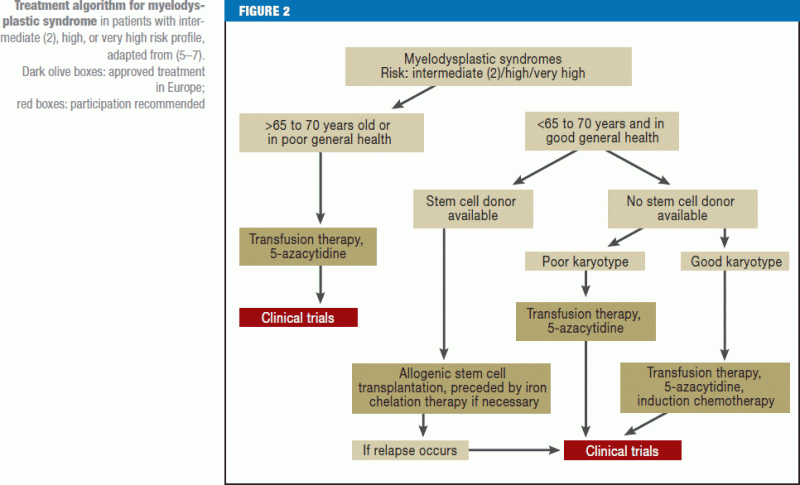
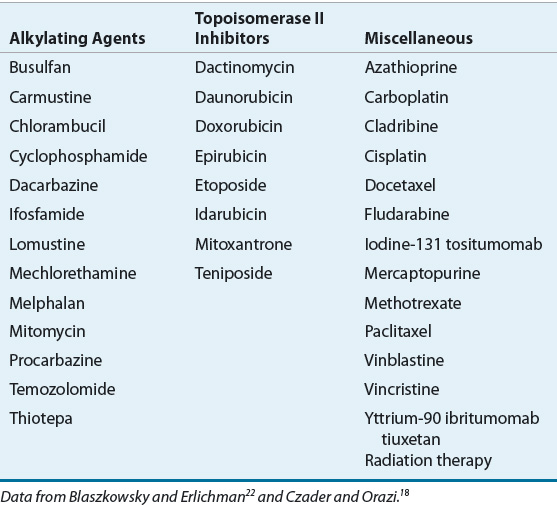
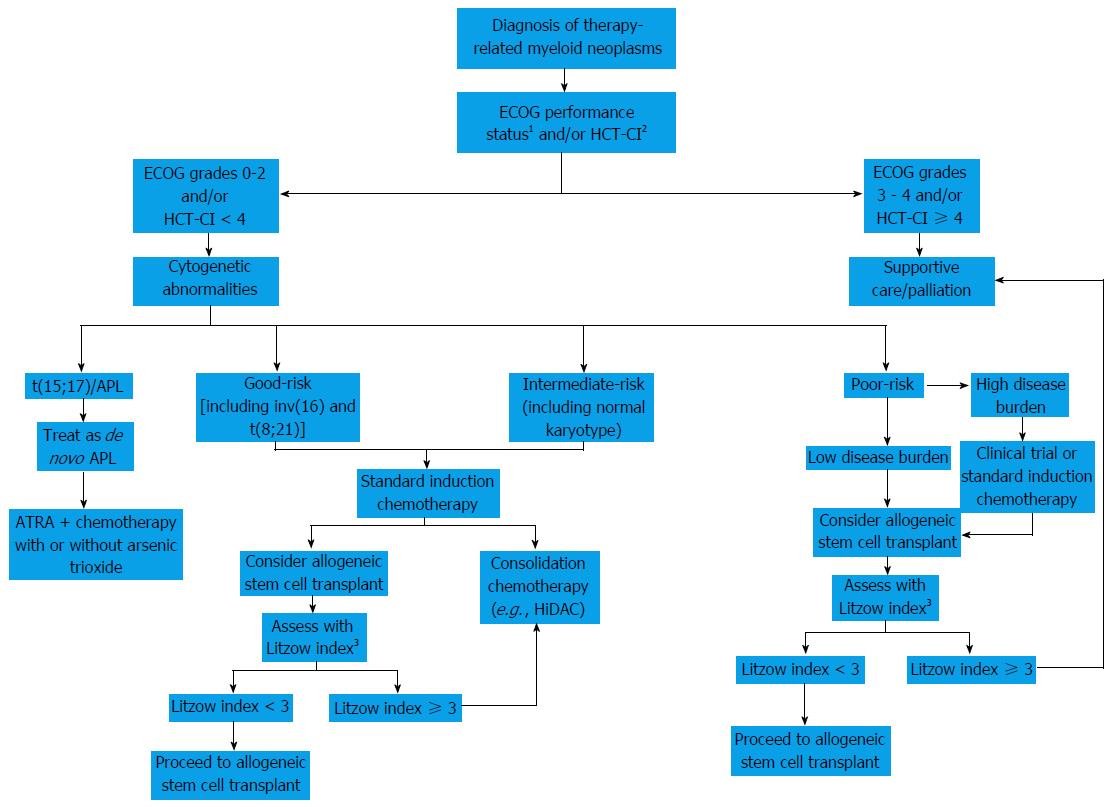
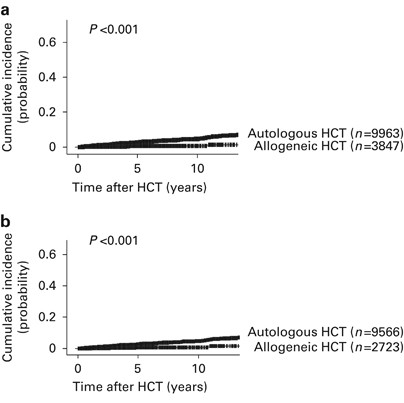
Drug therapy may be used to slow progression of the disease. Patients who are exposed to DNA-damaging agents including cytotoxic chemotherapy and radiation therapy are at risk for developing therapy-related myeloid neoplasms t-MN. We analyzed outcomes in 868 persons with t-AML n 545 or t-MDS n 323 receiving allogeneic transplants from 1990 to 2004.
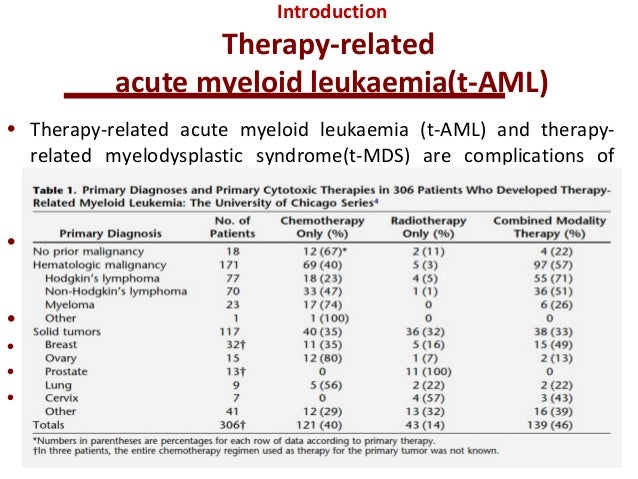
Between 1981 and 2006 461 patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid a median age of 40 years and a history of solid tumor n163 malignant lymphoma n133 or other hematologic diseases n57 underwent stem cell transplantation and their data were reported to the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Primary diagnoses were Hodgkins disease in two patients and ovarian carcinoma. These conditions comprise a continuum of diseases that includes therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia t-AML therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome t-MDS and therapy-related MDSmyeloproliferative neoplasms t-MDSMPN.
We have identified an identical reciprocal translocation between the long arms of chromosomes 3 and 21 with breakpoints at bands 3q26 and 21q22 t 321 q26q22 in the malignant cells from five adult patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome t-MDS or acute myeloid leukemia t-AML. The therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome can be treated through two methods chemotherapy and bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Secondary malignant neoplasms SMN are a major cause of premature death among cancer survivors 1.
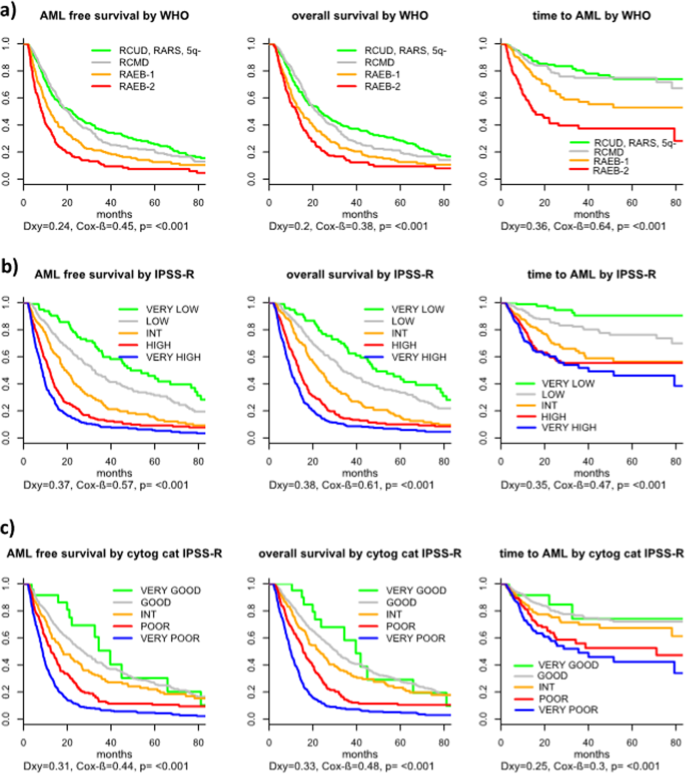
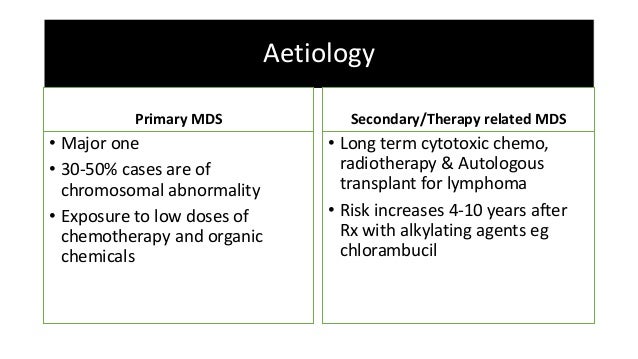
It is estimated that the incidence of tMDS or acute myeloid leukemia tAML ranges from 10 to 20 at 20 years following exposure to chemotherapy or radiation. Roughly 20 of MDS are therapy related t-MDS and this is considered an independent adverse prognostic factor. Myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is a heterogeneous clonal disorder characterized by deregulation of apoptosis dysplastic features in hematopoietic precursors peripheral blood cytopenias and an increased risk for transformation to acute leukemia.
Traditionally any myeloid neoplasm arising in a patient with a history of chemotherapy andor. Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms t-MNs include therapy-related cases of acute myeloid leukemia t-AML myelodysplastic syndromes t-MDS and myelodysplasticmyeloproliferative neoplasms t-MDSMPN that occur as a late complication of cytotoxic chemotherapy andor radiation therapy administered for a prior neoplastic or non-neoplastic disorder.
Therapy-related myeloid neoplasms t-MNs include therapy-related cases of acute myeloid leukemia t-AML myelodysplastic syndromes t-MDS and myelodysplasticmyeloproliferative neoplasms t-MDSMPN that occur as a late complication of cytotoxic chemotherapy andor radiation therapy administered for a prior neoplastic or non-neoplastic disorder.
Between 1981 and 2006 461 patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome or acute myeloid a median age of 40 years and a history of solid tumor n163 malignant lymphoma n133 or other hematologic diseases n57 underwent stem cell transplantation and their data were reported to the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. It is estimated that the incidence of tMDS or acute myeloid leukemia tAML ranges from 10 to 20 at 20 years following exposure to chemotherapy or radiation. Roughly 20 of MDS are therapy related t-MDS and this is considered an independent adverse prognostic factor. Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes t-MDSs and acute myeloid leukemia t-AML have a poor prognosis with conventional therapy. In practice cases of therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome t-MDS are often classified according to morphologic schemes used for de novo MDS. We have identified an identical reciprocal translocation between the long arms of chromosomes 3 and 21 with breakpoints at bands 3q26 and 21q22 t 321 q26q22 in the malignant cells from five adult patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome t-MDS or acute myeloid leukemia t-AML. The therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome can be treated through two methods chemotherapy and bone marrow or stem cell transplantation. Drug therapy may be used to slow progression of the disease. Patients with a myelodysplastic syndrome who have symptoms caused by low blood counts are given supportive care to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Myelodysplastic syndrome MDS is a heterogeneous clonal disorder characterized by deregulation of apoptosis dysplastic features in hematopoietic precursors peripheral blood cytopenias and an increased risk for transformation to acute leukemia. We studied 155 patients with. It includes hypomethylating agents such as Vidaza and Dacogen. We have identified an identical reciprocal translocation between the long arms of chromosomes 3 and 21 with breakpoints at bands 3q26 and 21q22 t 321 q26q22 in the malignant cells from five adult patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome t-MDS or acute myeloid leukemia t-AML. It is caused by treatment with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for a previous cancer. Roughly 20 of MDS are therapy related t-MDS and this is considered an independent adverse prognostic factor. Encouraging results are reported after allogeneic transplantation.




























Posting Komentar untuk "Therapy Related Myelodysplastic Syndrome"