 Myths about HIV and AIDS | Avert
Myths about HIV and AIDS | AvertCan HIV live and spread out of the body? HIV does not survive long outside the body, and cannot be reproduced without a human host. There is no single answer to the question of how long HIV can survive outside the body, as on surfaces, as it depends on several factors. A person can contract if the damaged tissue or a mucous membrane, such as the rectum, penis, vagina, or mouth, enters into contact with body fluids containing the virus. Only certain body fluids can carry HIV. These fluids :This article explores the factors that affect the survival time of HIV outside the body in different fluids. It also explains how the virus can and cannot transmit. HIV does not usually survive for a long time outside the body, where it cannot be reproduced. The virus quickly dies when exposed to light and air. Therefore, contact with dry blood or semen that has been out of the body does not usually pose a risk to contract HIV. HIV cannot survive in the air, so people cannot get the virus to share space with a person who has HIV. It is also not possible to get HIV from sharing seats, utensils or bed linen. The length of time the virus can survive outside the body depends on several factors, such as:Although the risk of contracting HIV from external fluids is low, the risk of sharing equipment to inject drugs, such as needles and syringes. The reason for this is that the person can inject blood that contains HIV directly into his bloodstream. Moderns are very effective in preventing HIV transmission. In most cases, the virus is under control within a person who initiates this treatment. Once the viral load—the amount of the virus in the blood—is undetectable, there is virtually no risk that the virus will transmit to other people through blood, semen or other body fluids. Compared to other fluids, the blood contains the highest concentrations of HIV. The virus quickly dies when it comes out of the body, so the risk of getting HIV from dry blood contact is low. In a medical environment, a person could get HIV if he gets a cut of a leaf or needle that has been in contact with blood that contains HIV. However, the risk of getting HIV in this way is . The risk of getting HIV from sharing equipment with injecting drugs is very high because a person could inject blood that contains HIV directly into the bloodstream. The virus can survive longer within a syringe than when exposed to the air. According to , there are 1 in 160 chances of getting HIV from using a needle that a person with HIV has used. For more information and in-depth resources on HIV and AIDS, visit us. Semen is the body fluid that contains the second highest concentration of HIV. According to the HIV charity, it is not possible for a person to contract HIV by contacting a condom that contains a person's sperm with the virus. The speed at which HIV dies outside a human host makes this impossible. While HIV can spread through vaginal fluids, the virus tends to exist in smaller concentrations than in blood and semen. It is not clear why this is the case, but it seems that hormones and cell types in the genital tract can play a role. Maternal milk contains HIV at lower concentrations than blood or semen. A baby can get HIV through breast milk, so it recommends that people with HIV are not breast-feeding, regardless of antiretroviral therapy or viral loading. HIV can also transmit to a baby through pregnancy or birth. However, this is becoming less and less common with recent developments in attention. If a person with HIV receives effective antiretroviral therapy, and gives HIV medication to the baby for 4 to 6 weeks after delivery, the risk of the baby who gets HIV can be. The most common forms of contracting HIV in the United States are by sharing equipment by injecting drugs and having anal or vaginal sex without barrier contraception. Anal sex poses a higher risk than vaginal sex, as there is a higher chance of tissue damage. Although less common, HIV can happen to a baby during pregnancy, birth or breastfeeding. In extremely rare cases, HIV can spread if the blood comes into contact with an open wound. There is a possibility that this will happen if the partners are involved in kissing open mouth, and both have hemorrhagic gums or sores open inside the mouth. However, the saliva that does not contain blood cannot transmit HIV. People can't get HIV out of their mouths or cheek kisses. People can reduce or eliminate the possibility of getting HIV using barrier contraception or taking HIV preventive therapy, known as PrEP is a pill that a person can take once a day to minimize the possibility of getting HIV. It can be useful for those who: It is not possible to get HIV from myths: Many and much disinformation surround the transmission of HIV. HIV cannot survive for a long time outside the human body, which means that the risk of getting HIV from dry blood or cum is low. If a person suspects that they have come into contact with HIV in the last 72 hours, he or she may use an emergency prevention method called . Learn how to test for HIV in the United States. Although there are inequalities between different regions and populations, modern antiretroviral therapy has made it possible for people with HIV to live long and healthy lives without the virus it transmits to others. Last medical review on 28 November 2020Most recent newsRelated coverage
Accessibility links Search results Hiv dies in the air? Yahoo answers Foot links
How long does HIV live outside the body?
How Long Does HIV Live Outside the Body: In Air, on Surfaces
How Long Does HIV Live Outside the Body: In Air, on Surfaces
Hiv 201111111
From exposure to infection: The biology of HIV transmission | CATIE - Canada's source for HIV and hepatitis C information
How Long Does HIV Live Outside the Body: In Air, on Surfaces
Impossible routes of HIV transmission | aidsmap
How long does HIV live outside the body?
How Long Does HIV Live Outside the Body: In Air, on Surfaces
HIV and Coinfections | Treatment, Care, and Prevention for People with HIV | Clinicians | HIV | CDC
Ways HIV is Not Transmitted | HIV Transmission | HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC
A quick breakdown on how HIV can be transmitted. | HIV
What Do You Really Know About HIV and AIDS?
How Long Does HIV Live Outside the Body: In Air, on Surfaces
How long does HIV live outside the body?
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection - Infections - MSD Manual Consumer Version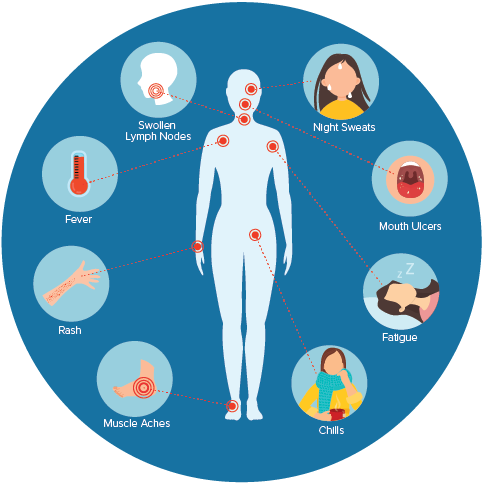
About HIV/AIDS | HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC
Myths about HIV and AIDS | Avert
How is HIV transmitted?
Chapter 24; Lesson 3. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) – a virus that attacks the immune system. Once HIV enters the body, it finds and destroys. - ppt download
How long does HIV live outside the body?
How HIV Affects the Body: HIV Transmission, Disease Progression & More
HIV/AIDS: The Basics
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) Infection - Infections - Merck Manuals Consumer Version
Ok people, when the HIV virus is exposed to air, it dies. Like if someone HIV
Protect Yourself from HIV/AIDS | SCDHEC
How Does the Coronavirus Behave Inside a Patient? | The New Yorker
H.I.V. Is Reported Cured in a Second Patient, a Milestone in the Global AIDS Epidemic - The New York Times
How long does HIV live outside the body?
The Virus - The Virus | The Age Of Aids | FRONTLINE | PBS
Other Health Issues of Special Concern for People Living with HIV | HIV.gov
Health sector spending and spending on HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, and development assistance for health: progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 3 - The Lancet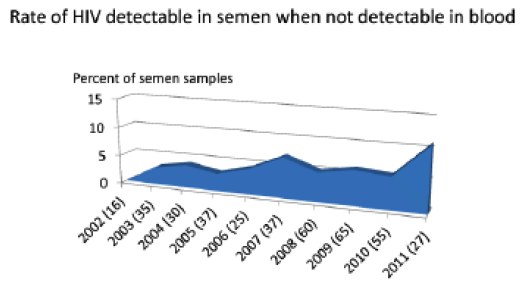
HIV Can Be Found in Semen Even When Viral Load Is Undetectable in Blood
Needlestick injuries, discarded needles and the risk of HIV transmission | aidsmap
HIV transmission | aidsmap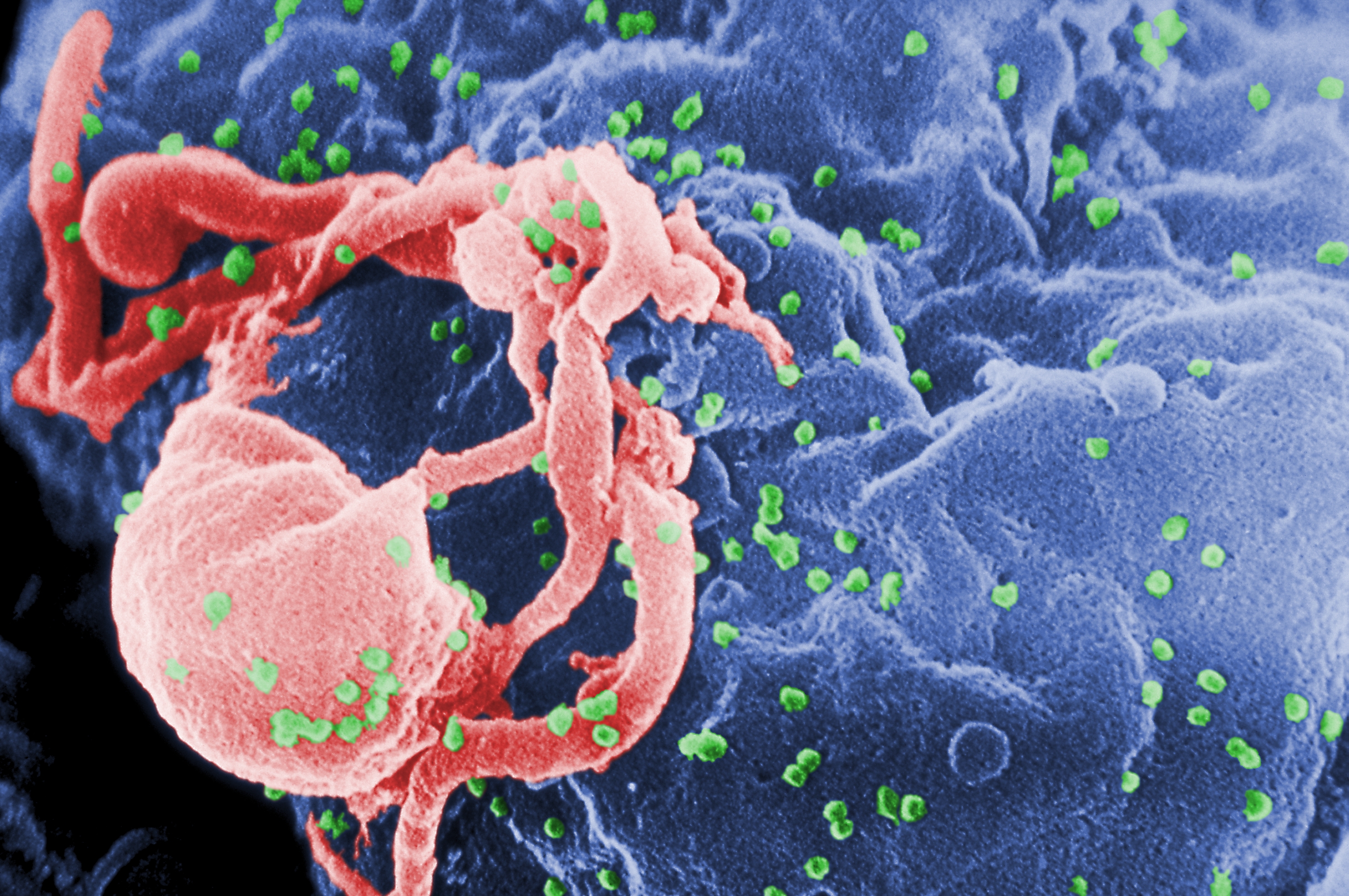
History of HIV/AIDS - Wikipedia
The Connection between TB and HIV | Pamphlets, Brochures, Booklets| Publications & Products | TB | CDC
How Long do 6 Common Bacteria and Viruses Last Outside the Body?
About HIV/AIDS | HIV Basics | HIV/AIDS | CDC
 Myths about HIV and AIDS | Avert
Myths about HIV and AIDS | Avert


































Posting Komentar untuk "does the hiv virus die when exposed to air"